A Chilly Conundrum: An Industrial Chiller System FAQ
How Do Chiller Systems Work?
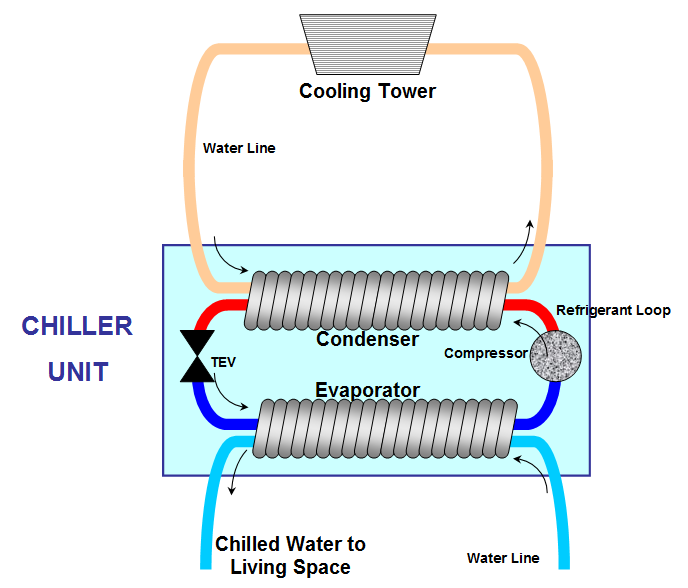
Chillers work by removing heat from liquids by bringing the heat from the building through a series of cooling loops. In this process, heat is transferred from the chiller to the condenser via a refrigerant. The cooled liquid then circulates back through heat exchangers to cool the equipment to ultimately be expelled out of the building through the cooling tower. In short, they provide a continuous stream of coolant to remove excess, unwanted heat from premises in an efficient and self-sustaining way.
Where Are They Used?
Chillers are commonly used in large industrial applications where cost and efficiency are important factors. This can include high-traffic buildings such as hotels, malls, and arenas or more specialized environments where there are heavy infrastructural demands such as power plants, manufacturing facilities, and corporations with extensive operations. In general, chillers are ideal in these environments, as they regulate the temperature for workers and extend the lifespan of critical machinery under regular stress.
What Are The Benefits Of Chillers?
—Enormous cooling output: Industrial chillers are large pieces of equipment that can sustainably cool large areas that regular HVAC systems could not. To put it in perspective, home AC units have a cooling capacity of between 5,000-34,000 BTU/hr depending on the size of the room needing cooling. In contrast, it is common to find industrial chillers exceeding 1,000,000 BTU/hr.
—Increased lifespan of equipment: In addition to being powerful pieces of equipment, they can greatly affect the surrounding equipment. Especially in high-stress mechanical environments, chillers can help regulate the temperature of surrounding equipment. This results over time in equipment that lasts longer and performs at a higher level.
—Reduced operational costs: Due to how chillers continuously circulate air and water in a cycle, they can contribute to lower energy costs and reduced operational costs. While chillers are a significant investment, the lifetime value of a chiller will save your business money and result in better and safer operating conditions for your staff.
Chillers, such as the one above can greatly improve a facility’s efficiency and reduce operating expenses.
Air-Cooled Vs. Water-Cooled Chillers:
The difference between air-cooled chillers and water-cooled chillers is that air-cooled chillers have a condenser that is cooled by ambient air while water-cooled chillers have water-cooled condensers that connect to the cooling towers. Water-cooled chillers are generally preferred in larger installations, as they tend to be more efficient over time and air-cooled chillers are ideal for smaller-scale projects depending on the needs of the company.
When Should I Replace My Chiller?
Here are a few things you should look for when deciding whether or not to replace your chiller:
The chiller is old (the older it is, the more likely it needs to be replaced)
You notice rising maintenance costs
You’re getting higher energy bills
It’s hard to find replacement parts
It is difficult for you or your employees to operate
For more detail, check out our article on the 5 must-know signs your chiller needs replacement.
Oxidation over time can put wear and tear on chillers, so it’s wise to proactively get your chillers inspected.
What Chiller Is Right For My Facility?
Finding the right chiller for your business is not an easy feat, but it’s not a decision you have to make alone.
With over 44 years of experience, our chiller experts will help you get an energy-efficient chiller that will help you run your business more reliably and save money in the process!
Ready to find the right energy-efficient chiller for you?